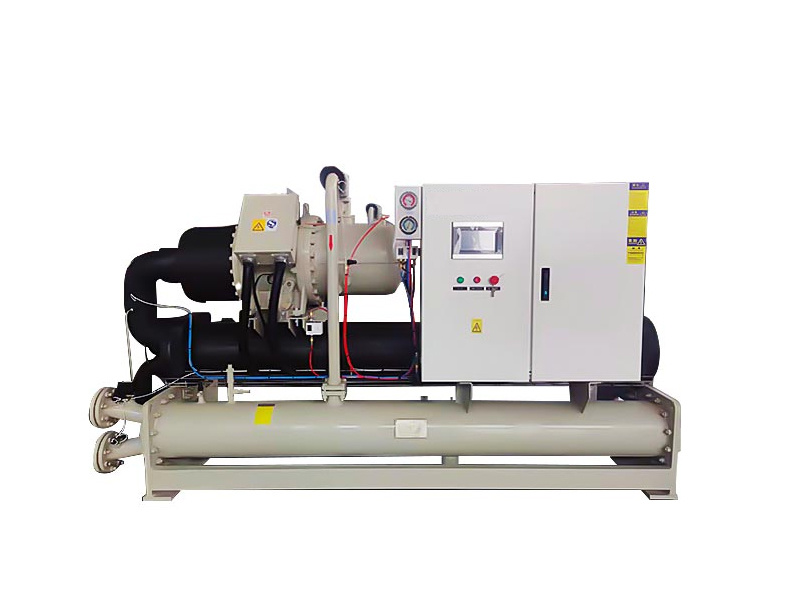
Understanding the Benefits of Low Temp Condensing Units in Industrial Refrigeration
2025-06-01 14:40
Understanding the Benefits of Low Temp Condensing Units in Industrial Refrigeration
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Low Temp Condensing Units
- 2. What Are Low Temp Condensing Units?
- 3. Advantages of Low Temp Condensing Units in Industrial Refrigeration
- 3.1 Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
- 3.2 Enhanced Performance in Industrial Settings
- 3.3 Positive Environmental Impact
- 3.4 Versatility Across Applications
- 4. Applications of Low Temp Condensing Units
- 5. Considerations for Selecting Low Temp Condensing Units
- 6. Maintenance Best Practices for Longevity
- 7. Future Trends in Low Temp Refrigeration Technology
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions
- 9. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Low Temp Condensing Units
Industrial refrigeration plays a pivotal role in various sectors, from food storage to pharmaceuticals. Low temp condensing units have emerged as vital components in this field, providing efficient and reliable cooling solutions. These systems are specifically designed to operate effectively at low temperatures, making them essential for industries requiring precise temperature control. Understanding the benefits of these units allows companies to optimize their refrigeration processes, enhance energy savings, and reduce environmental impact.
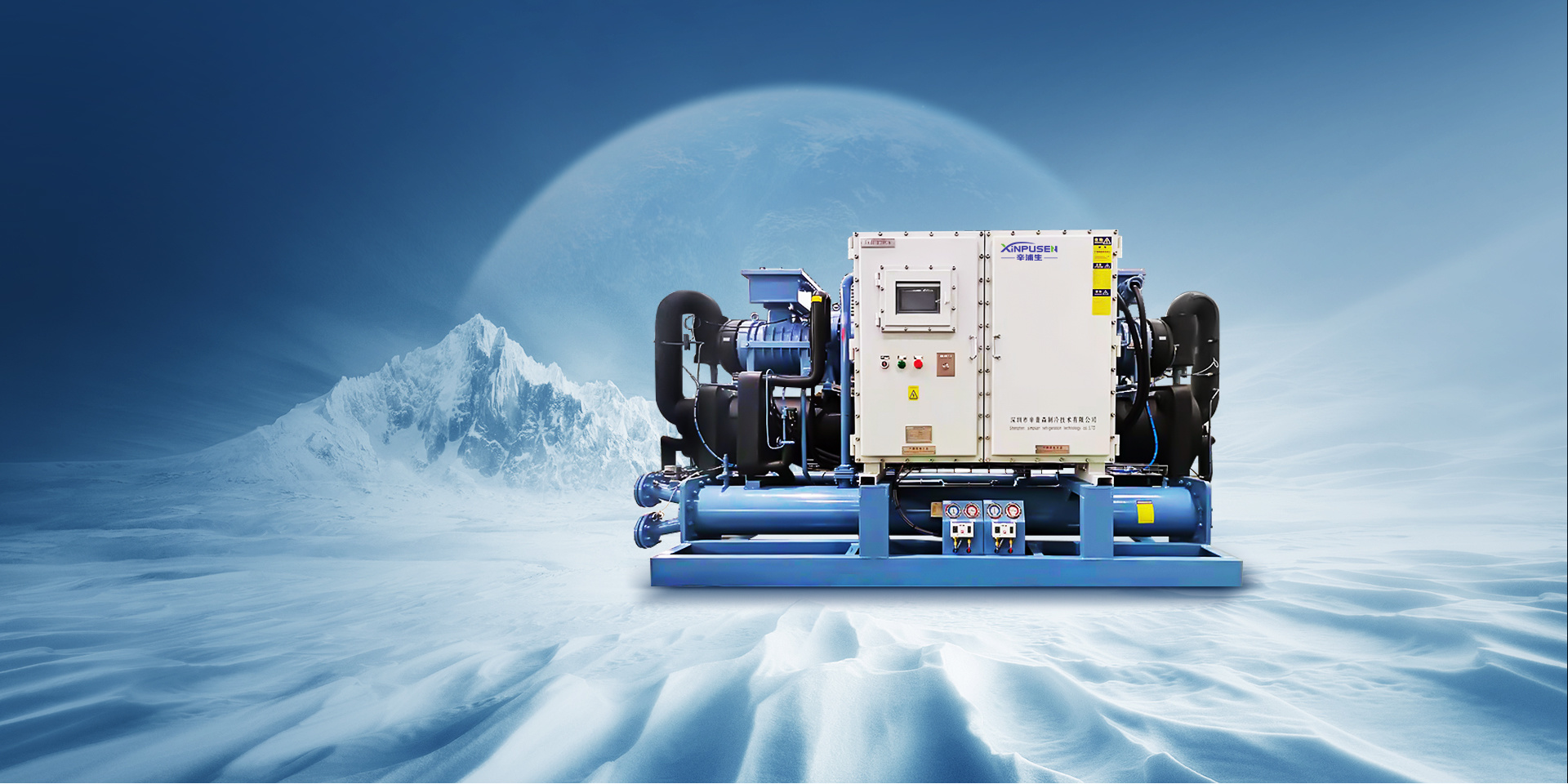
2. What Are Low Temp Condensing Units?
Low temp condensing units are refrigeration systems that utilize a compressor, condenser, and evaporator to maintain low temperatures. These units are engineered to operate efficiently at low ambient temperatures, typically below 32°F (0°C). They are commonly used in walk-in freezers, ice cream production facilities, and other cold storage applications.
One of the defining features of low temp condensing units is their ability to maintain consistent temperature levels, which is crucial for preserving perishable goods. The technology behind these units has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced controls and energy-efficient components to enhance performance while minimizing energy consumption.
3. Advantages of Low Temp Condensing Units in Industrial Refrigeration
3.1 Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the primary benefits of low temp condensing units is their energy efficiency. These units are designed to operate optimally under low-temperature conditions, which significantly reduces the energy required for cooling. By utilizing high-efficiency compressors and advanced heat exchangers, companies can achieve substantial savings on energy bills.
Furthermore, energy-efficient refrigeration systems often qualify for utility rebates and incentives, allowing businesses to recoup their investment more quickly. Low temp condensing units also contribute to lower overall operational costs by reducing wear and tear on components, leading to less frequent maintenance and replacement needs.
3.2 Enhanced Performance in Industrial Settings
Low temp condensing units are engineered for performance under demanding industrial conditions. These units are capable of maintaining stable temperature levels even during peak operational hours, ensuring that products remain in optimal conditions. This reliability is crucial for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, where temperature fluctuations can lead to spoilage or product degradation.
Additionally, advanced control systems incorporated in low temp condensing units allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments. This feature enhances operational efficiency, reduces the likelihood of system failures, and increases overall productivity.
3.3 Positive Environmental Impact
As industries face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, low temp condensing units align well with environmental goals. These units often utilize refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP), helping companies minimize their environmental impact. By transitioning to energy-efficient systems, businesses can significantly reduce their carbon footprint while promoting sustainability.
Moreover, the reduction in energy consumption directly correlates with fewer greenhouse gas emissions, making low temp condensing units a responsible choice for environmentally-conscious businesses.
3.4 Versatility Across Applications
Low temp condensing units are incredibly versatile, making them suitable for various industrial applications. Whether used in food storage facilities, chemical processing, or cold logistics, these systems can be tailored to meet specific cooling requirements. Their ability to function in diverse environments allows businesses to streamline their operations and enhance overall efficiency.
From small-scale operations to large industrial complexes, low temp condensing units can be configured to accommodate varying load capacities. This flexibility is essential for businesses looking to scale operations while maintaining effective refrigeration solutions.
4. Applications of Low Temp Condensing Units
Low temp condensing units find applications across numerous industries, each benefiting from the unique advantages these systems offer:
- **Food and Beverage Industry**: Essential for preserving perishable goods, low temp units maintain optimal temperatures in refrigerated warehouses and processing plants.
- **Pharmaceuticals**: Critical for storing temperature-sensitive medications and vaccines, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
- **Chemical Processing**: Utilized for providing precise cooling in processes that require specific temperature control to maintain product integrity.
- **Logistics and Distribution**: Employed in refrigerated trucks and shipping containers to ensure products remain fresh during transport.
The adaptability of low temp condensing units makes them indispensable across various sectors, contributing to operational efficiency and product safety.
5. Considerations for Selecting Low Temp Condensing Units
When choosing the right low temp condensing unit for industrial refrigeration, several factors should be taken into account:
- **Capacity Requirements**: Evaluate the cooling load to select a unit that can adequately meet your specific needs.
- **Energy Efficiency Ratings**: Look for units with high energy efficiency ratings to ensure long-term savings on operational costs.
- **Refrigerant Type**: Consider the environmental impact of the refrigerant used and opt for low-GWP options when possible.
- **Installation and Maintenance**: Assess installation requirements and ease of maintenance to ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
- **Manufacturer Reputation**: Choose a reputable manufacturer known for quality products and reliable customer service.
Taking these factors into account will help ensure that the selected unit meets operational demands while promoting energy efficiency and sustainability.
6. Maintenance Best Practices for Longevity
Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of low temp condensing units. Here are some best practices to follow:
- **Regular Inspections**: Schedule routine inspections to identify potential issues before they escalate. Check for leaks, unusual noises, or performance drops.
- **Clean Coils**: Keep the condenser and evaporator coils clean to enhance heat exchange efficiency. Dust and debris can significantly hinder performance.
- **Monitor Refrigerant Levels**: Regularly check refrigerant levels to ensure optimal performance. Low refrigerant levels can lead to inefficiencies and system failure.
- **Replace Filters**: Change air filters as needed to maintain airflow and improve energy efficiency.
- **Professional Servicing**: Engage qualified technicians for annual servicing to address any complex issues and ensure the unit operates at peak performance.
Implementing these maintenance practices can extend the life of low temp condensing units and reduce the risk of costly repairs.
7. Future Trends in Low Temp Refrigeration Technology
The landscape of industrial refrigeration is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increasing environmental awareness. Here are some future trends to watch in low temp refrigeration technology:
- **Smart Refrigeration Systems**: The integration of IoT technology will allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
- **Natural Refrigerants**: The shift towards natural refrigerants, such as CO2 and ammonia, is gaining momentum as industries seek sustainable alternatives to traditional refrigerants.
- **Modular Systems**: Modular refrigeration units that can be easily expanded or adapted to changing cooling needs will become more prevalent, offering flexibility for growing operations.
- **Energy Recovery Systems**: Technologies that capture and utilize waste heat from refrigeration processes will further enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational costs.
These trends represent the direction of the refrigeration industry, focusing on sustainability, efficiency, and adaptability.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical lifespan of a low temp condensing unit?
The lifespan of a low temp condensing unit generally ranges from 15 to 20 years, depending on factors such as maintenance, usage, and operating conditions.
Can low temp condensing units be used in varying climates?
Yes, low temp condensing units are designed to operate efficiently in various climates, but proper selection and installation are crucial for optimal performance.
What kind of maintenance do low temp condensing units require?
Regular maintenance includes inspections, cleaning coils, monitoring refrigerant levels, and changing filters. Annual professional servicing is recommended for complex issues.
Are low temp condensing units energy efficient?
Yes, low temp condensing units are designed for energy efficiency, often incorporating high-efficiency compressors and heat exchangers to minimize energy consumption.
What industries benefit most from low temp condensing units?
Industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, and logistics benefit significantly from low temp condensing units due to their precise temperature control capabilities.
9. Conclusion
Low temp condensing units are integral to modern industrial refrigeration, offering numerous benefits such as energy efficiency, enhanced performance, and environmental sustainability. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of these systems in maintaining product quality and reducing operational costs cannot be overstated. By understanding the advantages and applications of low temp condensing units, businesses can make informed decisions that align with both their operational needs and sustainability goals. Embracing advanced refrigeration technology will not only improve efficiency but also contribute to a greener future for the industrial sector.
Previous: Understanding Cryogenic Chiller Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
More Information
2026-03-02
Understanding the Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers for Industrial Applications
2026-02-24
quality air cooled industrial chiller
2026-02-23
Essential Insights into Air Cooled Industrial Chillers: Efficiency, Selection, and Maintenance
2026-02-16
What to Expect During the Installation of Air Cooled Industrial Chillers: A Comprehensive Guide
2026-03-02
Understanding the Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers for Industrial Applications









 CN
CN EN
EN