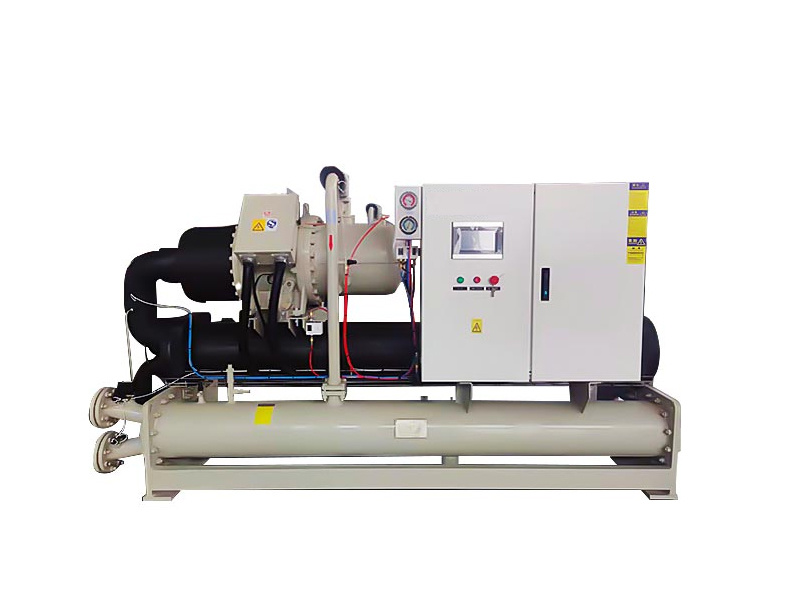
Air-Cooled Magnetic Levitation Chillers vs. Water-Cooled Chillers: Which Is Better?
2025-07-25 20:20
Air-Cooled Magnetic Levitation Chillers vs. Water-Cooled Chillers: Which Is Better?
The choice between air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers and water-cooled chillers can be daunting for businesses looking to optimize their cooling systems. With advances in technology and a growing emphasis on energy efficiency, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each type is crucial. In this article, we will explore these two cooling solutions in depth, enabling you to make a well-informed decision tailored to your industrial needs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Chillers
- Understanding Chillers
- Air-Cooled Chillers: An Overview
- What is Magnetic Levitation Technology?
- Water-Cooled Chillers: An Overview
- Efficiency Comparison: Air-Cooled vs. Water-Cooled
- Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Costs
- Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
- Maintenance Requirements: Long-Term Considerations
- Case Studies: Application Scenarios
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Chillers
Chillers are integral components in various industrial applications, providing essential cooling for processes, facilities, and equipment. As industries evolve, the demand for efficient, reliable, and sustainable cooling solutions grows. Two popular options have emerged: air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers and water-cooled chillers. Each has its own unique features and advantages, making it vital to understand how they compare against one another.
Understanding Chillers
Before diving into specifics, it's important to understand what chillers are and how they function. Chillers remove heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. This cooled liquid is then circulated through a heat exchanger to absorb heat from the environment, providing the necessary cooling effect.
Chillers are categorized into two primary types: air-cooled and water-cooled. Air-cooled chillers use ambient air to cool the refrigerant, while water-cooled chillers use water from a cooling tower or a similar source. With the development of magnetic levitation technology, air-cooled chillers have taken on a new form, offering various benefits.
Air-Cooled Chillers: An Overview
Air-cooled chillers have been the go-to choice in many applications due to their simplicity and ease of installation. These systems utilize fans to draw ambient air over the condenser coils, which cools the refrigerant before it cycles back into the evaporator. They are particularly effective in locations where water resources are scarce or expensive.
Advantages of Air-Cooled Chillers
- Cost-Effective Installation: Air-cooled chillers do not require complex water piping systems, making them less expensive to install.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: With fewer components than water-cooled systems, air-cooled chillers generally incur lower maintenance expenses.
- Versatility: They can be installed in various environments, including rooftops or outside buildings, providing flexibility in design.
Disadvantages of Air-Cooled Chillers
- Efficiency Limitations: Air-cooled chillers may struggle to achieve the same efficiency levels as water-cooled systems, particularly in high-demand situations.
- Noise Levels: The operation of fans can generate significant noise, which may not be suitable for all environments.
What is Magnetic Levitation Technology?
Magnetic levitation technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in the realm of air-cooled chillers. Instead of traditional mechanical components, magnetic levitation chillers use magnetic fields to suspend the compressor rotor. This eliminates mechanical friction, resulting in substantial energy savings and reduced wear and tear.
Benefits of Magnetic Levitation Technology
- Energy Efficiency: These chillers can operate more efficiently, often achieving lower energy consumption than traditional air-cooled models.
- Reduced Noise: With fewer moving parts, magnetic levitation chillers tend to operate more quietly, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
- Longer Lifespan: The absence of friction leads to less maintenance and a longer operational life.
Water-Cooled Chillers: An Overview
Water-cooled chillers offer an alternative solution, utilizing water from a cooling tower to absorb heat. This method allows for greater heat exchange efficiency, making them a preferred choice in larger facilities with high cooling demands.
Advantages of Water-Cooled Chillers
- Higher Efficiency: Water-cooled systems often achieve higher efficiencies, especially in large-scale operations.
- Lower Operating Costs: Although the initial investment is higher, lower energy costs can make water-cooled chillers more economical over time.
Disadvantages of Water-Cooled Chillers
- Complex Installation: They require more extensive piping and cooling tower installations, increasing upfront costs.
- Water Usage: These systems rely heavily on water resources, which may be limited or costly in some regions.
Efficiency Comparison: Air-Cooled vs. Water-Cooled
When it comes to efficiency, the choice between air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers and water-cooled chillers often hinges on the specific application and operational environment.
Performance Metrics
Air-cooled chillers typically exhibit lower efficiency ratings in high ambient temperatures compared to water-cooled systems. However, the introduction of magnetic levitation technology has narrowed this gap significantly. For facilities that require consistent and high-output cooling, water-cooled chillers may still hold an advantage due to their superior heat transfer capabilities.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Air-cooled chillers, particularly those utilizing magnetic levitation technology, often consume less energy due to their enhanced operational efficiencies. This can contribute to a lower carbon footprint and is increasingly important for companies looking to adopt sustainable practices. Water-cooled systems, while efficient, may require additional energy for cooling tower operation, impacting overall sustainability efforts.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Costs
Choosing between air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers and water-cooled chillers involves a thorough cost analysis, encompassing both initial investment and long-term operating costs.
Initial Investment
Air-cooled chillers generally have a lower initial cost due to simpler installation processes. However, water-cooled chillers might offer a better return on investment in high-demand applications where efficiency pays off over time.
Operating Costs
Operating costs are crucial when evaluating chiller options. Water-cooled chillers typically have lower operating costs in large-scale applications due to their efficiencies. However, air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers, while potentially higher in upfront costs, can lead to significant savings in electricity and maintenance in the long run.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
As companies increasingly prioritize sustainability, the environmental impact of cooling solutions becomes more critical. Air-cooled chillers, particularly those featuring magnetic levitation technology, are often seen as more environmentally friendly due to their reduced energy consumption and lower refrigerant usage.
Water Usage and Waste
Water-cooled chillers necessitate consistent water supplies, raising concerns in arid regions. Additionally, they can generate water waste if not managed properly. In contrast, air-cooled systems minimize water usage, aligning better with sustainability goals in water-scarce areas.
Maintenance Requirements: Long-Term Considerations
Maintenance is a crucial factor in the lifespan and efficiency of chillers. Understanding the maintenance requirements of both systems can help inform your decision.
Air-Cooled Chillers
Air-cooled chillers generally require less maintenance because they lack the complex water piping and cooling towers found in their water-cooled counterparts. Regular cleaning of condenser coils and inspection of fans are typically sufficient to keep them running efficiently.
Water-Cooled Chillers
Water-cooled chillers require more extensive maintenance due to their components, including cooling towers and water treatment systems. Regular checks for water quality and the potential need for chemical treatments can add to operational complexity.
Case Studies: Application Scenarios
Understanding real-world applications of both air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers and water-cooled chillers offers valuable insights into their effectiveness in various industries.
Industry Examples
In a manufacturing context, a facility that prioritizes energy efficiency and lower noise levels may opt for an air-cooled magnetic levitation chiller. Conversely, a large data center with high cooling demands may benefit more from a water-cooled chiller for its efficiency and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers more energy-efficient than traditional air-cooled chillers?
Yes, magnetic levitation chillers generally offer higher energy efficiency due to reduced mechanical friction, leading to lower operational costs.
2. What industries benefit most from water-cooled chillers?
Industries with high cooling demands, such as data centers, hospitals, and large manufacturing facilities, often benefit from water-cooled chillers due to their efficiency.
3. Can air-cooled chillers operate in humid climates effectively?
While air-cooled chillers can function in humid climates, their efficiency may decrease compared to drier conditions. Magnetic levitation technology can help mitigate some efficiency loss.
4. How often should chillers be maintained?
Maintenance schedules vary by type and model, but generally, air-cooled chillers should be inspected at least bi-annually, while water-cooled systems may require more frequent checks due to their complexity.
5. What is the lifespan of air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers?
With proper maintenance, air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers can last upwards of 15-20 years, significantly longer than traditional models.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers and water-cooled chillers possess unique advantages and drawbacks that cater to different industrial needs. **Air-cooled magnetic levitation chillers** stand out for their energy efficiency, lower maintenance costs, and reduced environmental impact, while **water-cooled chillers** excel in large-scale applications with high cooling demands. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific operational requirements, facility constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. By weighing these factors carefully, you can make an informed decision that meets your cooling needs effectively.
Previous: Understanding Air-Cooled Screw Chiller Heat Pumps: Efficiency and Applications
More Information
2026-03-02
Understanding the Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers for Industrial Applications
2026-02-24
quality air cooled industrial chiller
2026-02-23
Essential Insights into Air Cooled Industrial Chillers: Efficiency, Selection, and Maintenance
2026-02-16
What to Expect During the Installation of Air Cooled Industrial Chillers: A Comprehensive Guide
2026-03-02
Understanding the Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers for Industrial Applications









 CN
CN EN
EN