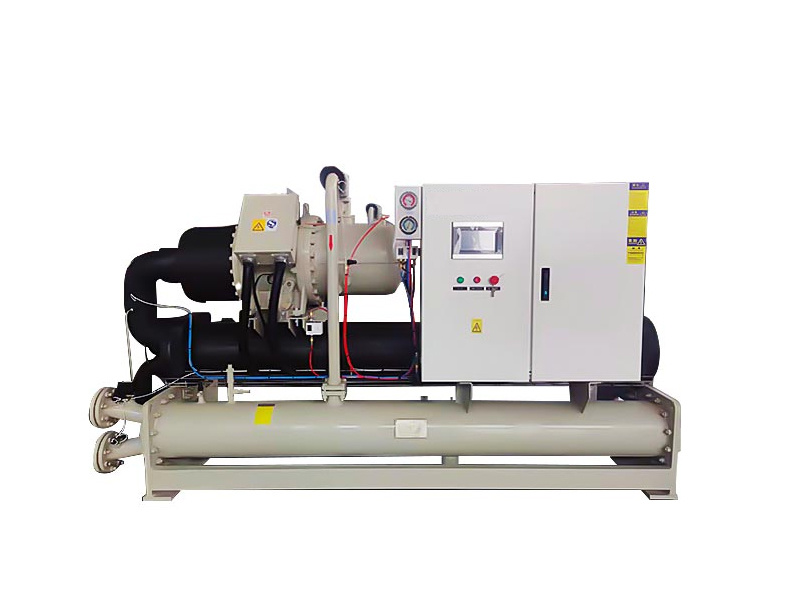
How Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers Revolutionize Cooling Processes
2025-11-10 10:50
How Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers Revolutionize Cooling Processes
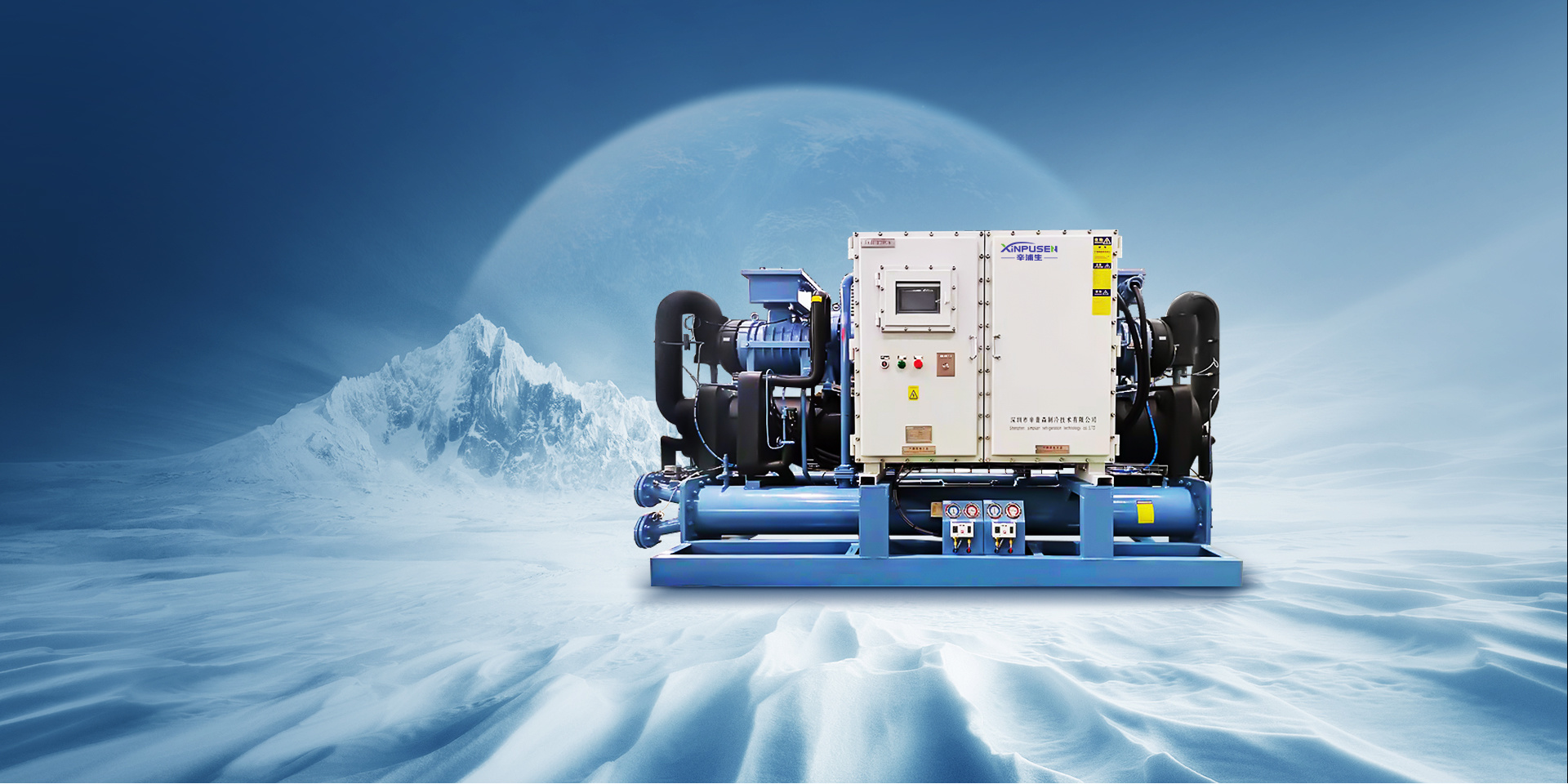
In the constantly evolving landscape of industrial cooling technologies, **ultra-low temperature cascade chillers** have emerged as pivotal solutions for various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, and food and beverage industries. These advanced chillers not only deliver efficient cooling but also provide precise temperature control, making them essential for processes that require stringent temperature management. This article delves into the mechanics, advantages, applications, and future prospects of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of their revolutionary impact on cooling processes.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Cascade Chillers
- The Mechanics of Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers
- Advantages of Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers
- Applications of Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers
- Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
- Maintenance and Reliability
- Future Trends in Cooling Technology
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding Cascade Chillers
Cascade chillers are specialized refrigeration systems comprising two or more refrigeration cycles arranged in a series. This design allows for highly efficient cooling over a broader temperature range. Unlike traditional chillers, which operate on a single refrigeration cycle, cascade chillers utilize two or more refrigerants with different boiling points. This enables them to achieve ultra-low temperatures, essential for applications that require precise thermal regulation.
The Essential Components of Cascade Chill Systems
A typical cascade chiller consists of several key components:
- Evaporators: These absorb heat from the process fluid, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the system.
- Compressors: These increase the pressure of the refrigerant vapor, thereby raising its temperature before it enters the condenser.
- Condensers: These cool and condense the refrigerant vapor back into liquid form, allowing for heat rejection.
- Expansion Devices: These reduce the pressure of the refrigerant, allowing it to flow into the evaporator at a lower temperature.
The Mechanics of Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers
The operation of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers involves two primary refrigeration cycles. The first cycle utilizes a refrigerant with a relatively higher boiling point, cooling down to a temperature that is effective for general applications. Subsequently, the second cycle employs a refrigerant with a lower boiling point, enabling the system to achieve the ultra-low temperatures necessary for sensitive processes.
Process Flow of Cascade Chillers
The process flow in an ultra-low temperature cascade chiller can be summarized in the following steps:
- **Heat Absorption:** The evaporator of the first cycle absorbs heat from the process fluid.
- **Compression:** The compressor raises the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant vapor.
- **Heat Rejection:** The condenser rejects heat to the external environment, condensing the refrigerant back into liquid form.
- **Expansion and Lowering Temperature:** The expansion valve reduces the pressure, allowing the refrigerant to enter the evaporator of the second cycle, where it absorbs additional heat and provides ultra-low temperatures.
Advantages of Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers
Ultra-low temperature cascade chillers present numerous advantages that make them invaluable in industrial cooling applications:
1. Exceptional Temperature Control
These chillers provide precise temperature control, crucial for processes such as **cryopreservation** and **sensitive chemical reactions**. With capabilities to achieve temperatures as low as -80°C or even lower, they cater to the stringent requirements of modern industrial applications.
2. Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Operating at lower temperatures can lead to significant energy savings. Cascade chillers are designed to optimize energy use, which results in lower operational costs over time.
3. Versatility in Various Applications
Ultra-low temperature cascade chillers are adaptable to a wide range of applications, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food processing. Their versatility allows industries to maintain the integrity and quality of temperature-sensitive products.
4. Environmentally Friendly Solutions
Many modern cascade chillers utilize eco-friendly refrigerants, reducing the environmental impact associated with cooling processes. This advancement aligns with global sustainability efforts and regulations.
Applications of Ultra-Low Temperature Cascade Chillers
The unique capabilities of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers make them suitable for various critical applications:
1. Pharmaceutical and Biotech Industries
In the pharmaceutical sector, maintaining precise temperatures is vital for storing vaccines and biological samples. Ultra-low temperature cascade chillers ensure that these sensitive products remain stable and effective.
2. Cryogenic Applications
These chillers are indispensable in applications requiring cryogenic temperatures, such as **cryopreservation of cells and tissues**. Their ability to achieve ultra-low temperatures ensures the safe storage of biological samples.
3. Food and Beverage Preservation
The food industry relies on ultra-low temperature cascade chillers to preserve the quality and safety of products. By maintaining low temperatures, these chillers extend shelf life and prevent spoilage.
4. Research and Development
In research facilities, ultra-low temperature cascade chillers are used to create controlled environments for experiments. They facilitate temperature-sensitive experiments, ensuring reliable results.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the standout features of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers is their energy efficiency. The design encourages low power consumption while delivering high cooling capacities. This efficiency translates into substantial cost savings over time, making them an attractive investment for industries.
Understanding the Cost-Effectiveness of Cascade Chillers
Investing in an ultra-low temperature cascade chiller can yield long-term financial benefits by:
- Reducing energy bills through optimized energy usage.
- Lowering maintenance costs due to fewer breakdowns and improved reliability.
- Extending equipment life through effective heat management.
Maintenance and Reliability
To ensure optimal performance, regular maintenance of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers is essential. However, the reliability of these systems is inherently higher due to their advanced design and efficient operation. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Routine inspections of refrigerant levels and pressure.
- Cleaning or replacing filters to ensure efficient airflow.
- Checking and maintaining compressor functionality.
Maximizing Reliability Through Technologies
Modern chillers are equipped with intelligent monitoring systems that provide real-time data on performance and maintenance needs, allowing for preemptive action to be taken before serious issues arise.
Future Trends in Cooling Technology
The future of cooling technology lies in the continued innovation of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers. Trends to watch include:
- Integration of IoT: Smart chillers with Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities will allow for remote monitoring and control, enhancing efficiency and usability.
- Advancements in Refrigerants: The ongoing development of eco-friendly refrigerants will contribute to more sustainable cooling solutions.
- Modular Systems: Future chillers may adopt modular designs for easier scalability and customization, catering to diverse industrial needs.
Conclusion
Ultra-low temperature cascade chillers are revolutionizing cooling processes across various industries by providing exceptional temperature control, energy efficiency, and reliability. Their ability to achieve ultra-low temperatures makes them indispensable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research. As technology continues to evolve, these chillers will play an increasingly vital role in maintaining optimal conditions for temperature-sensitive applications. Investing in ultra-low temperature cascade chillers is not just a choice for today; it is a strategic decision for a sustainable and efficient future in industrial cooling.
FAQs
1. What is the operating temperature range of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers?
Ultra-low temperature cascade chillers can typically operate at temperatures as low as -80°C or even lower, depending on the specific design and refrigerants used.
2. How do cascade chillers differ from traditional chillers?
Unlike traditional chillers that operate on a single refrigeration cycle, cascade chillers use multiple cycles with different refrigerants, allowing for greater efficiency and the ability to reach lower temperatures.
3. Are ultra-low temperature cascade chillers energy-efficient?
Yes, these chillers are designed to optimize energy consumption, resulting in significant energy savings and lower operational costs over time.
4. What industries benefit the most from ultra-low temperature cascade chillers?
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage processing, and research laboratories significantly benefit from the precision and efficiency of ultra-low temperature cascade chillers.
5. How can I maintain my ultra-low temperature cascade chiller?
Regular maintenance includes checking refrigerant levels, cleaning or replacing filters, and inspecting compressor functionality. Implementing smart monitoring technologies can also enhance maintenance efforts.
Previous: Understanding Hot and Cold Integrated Temperature Control Units: A Key to Efficient Industrial Cooling
More Information
2026-03-02
Understanding the Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers for Industrial Applications
2026-02-24
quality air cooled industrial chiller
2026-02-23
Essential Insights into Air Cooled Industrial Chillers: Efficiency, Selection, and Maintenance
2026-02-16
What to Expect During the Installation of Air Cooled Industrial Chillers: A Comprehensive Guide
2026-03-02
Understanding the Advantages of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers for Industrial Applications









 CN
CN EN
EN